Introduction
Every teacher has faced that moment—students off-task, noise levels climbing, and a lesson teetering on the edge of collapse. Managing behaviour in the classroom isn’t just about maintaining order—it’s about creating an environment where learning thrives. With the right blend of behaviour management techniques, structured class rules, adaptable, and innovative teaching styles and tools, teachers can turn chaos into calm. Whether you’re a new educator or a seasoned professional, this blog explores actionable strategies to tackle common behaviour management problems and support positive behaviour.
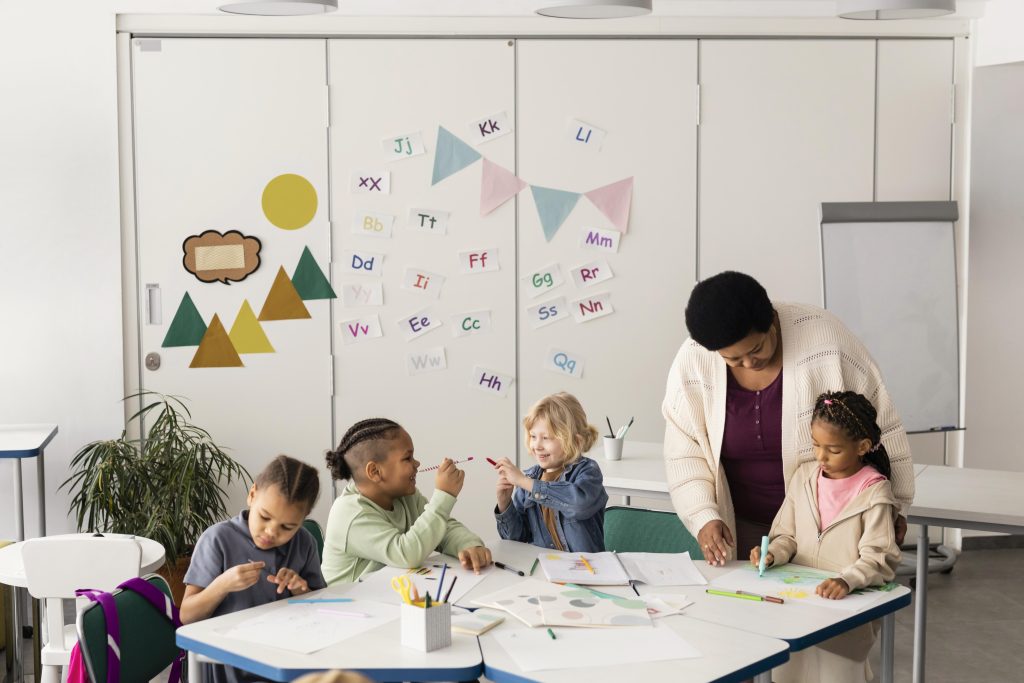

The Root of Behaviour Management Problems
Before solutions, it’s essential to identify the source. Common problems in behaviour stem from:
- • Undefined or inconsistent class rules
- • Mismatch between style of teaching and student needs
- • Lack of engaging tools of teaching
- • Poor classroom layout or structure
- • Emotional or social factors influencing student behaviour
Understanding the “why” behind disruptive behaviours is the first step in resolving them. For example, a student who frequently calls out may be seeking attention or struggling to follow the pace of instruction.

Effective Behaviour Management Techniques
Once the root causes are clear, it’s time to apply techniques of behaviour management that make a real difference. Some of the most effective include:
- • Proximity control: Simply standing near a student often redirects their focus.
- • The ‘choice’ technique: Offering two positive options helps reduce defiance.
- • Non-verbal cues: Eye contact, hand signals, or a silent countdown can shift behaviour without interrupting the flow.
- • Positive reinforcement: Catch students doing the right thing and praise it.
- • Structured transitions: Use timers or countdowns to manage movement and attention.
These techniques not only prevent escalation but also build student confidence and autonomy.
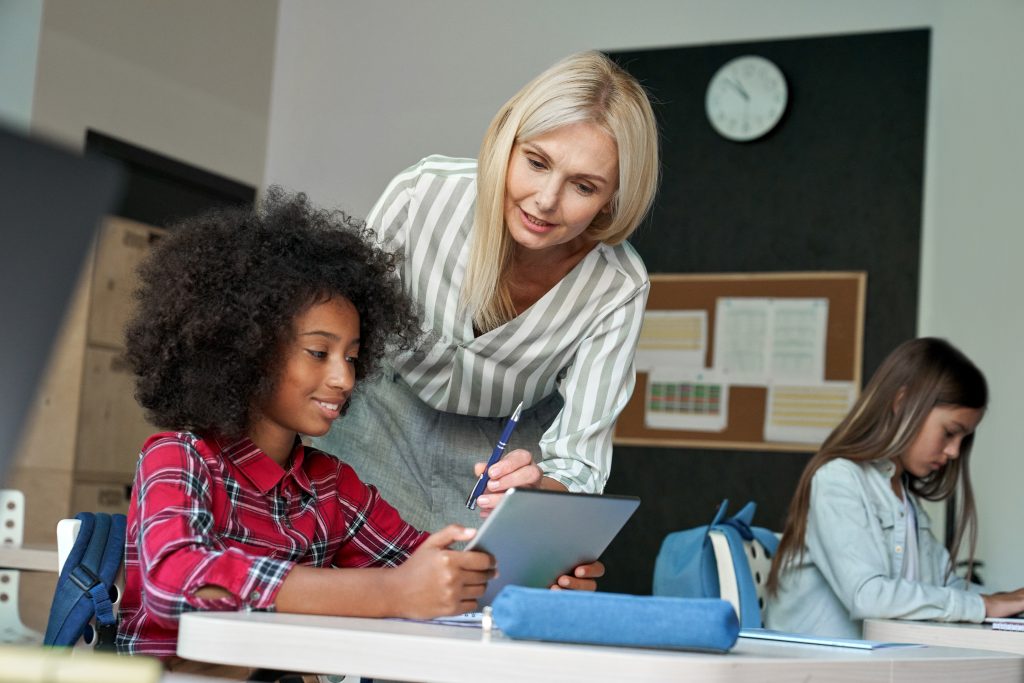

Building Strong Class Rules
Classroom rules aren’t just about control—they shape classroom culture. Effective rules are:
- • Clear and concise: “Be kind. Be safe. Be ready to learn.”
- • Positively framed: Say what to do, not just what not to do.
- • Consistent reinforcement: Praise compliance and address violations calmly.
- • Collaboratively created: Letting students help define rules increases buy-in.
Rules are the backbone of classroom management and should be taught, rehearsed, and revisited regularly.

Positive Behaviour Support in Action
Supporting positive behaviours help in reinforcing desired behaviours. Key elements include:
- • Preventive strategies: Arranging the environment to reduce triggers.
- • Clear expectations: Posting and practicing what good behaviour looks like.
- • Tiered interventions: Extra support for students needing more help.
- • Data-driven decisions: Tracking patterns to inform changes.
PBS helps create classrooms where students know what’s expected and feel motivated to meet those expectations. Research shows that teachers who routinely reflect on their practice see up to a 27% reduction in off task behaviour, underscoring the transformative power of simple, structured reflection .

Leveraging Teaching Tools for Better Behaviour
Modern tools of teaching can revolutionize classroom management:
- • Tracking apps (e.g., ClassDojo, LiveSchool) offer immediate feedback.
- • Timers and visual schedules help manage time and transitions.
- • Calm-down corners provide space for students to self-regulate.
- • Interactive tech (like smartboards and learning apps) keeps students engaged and focused.
The right tools align with your goals and reduce the need for repeated reminders or corrections.

The Role of Teaching Styles in Behaviour Management
- • Authoritative: Balanced—high expectations with high support. Great for structure.
- • Democratic: Encourages responsibility and choice. Fosters independence.
- • Facilitator: Hands-off but supportive—ideal for collaborative projects.
- • Directive: Clear leadership. Useful for younger or less self-regulated learners.
Adapting your style to the students and subject can preempt many problems in behaviour management.

Your style of teaching can either calm or contribute to classroom issues. Here’s how different styles affect management:
Choosing the Right Method of Teaching
The teaching methods influence student behaviour more than we often realize. Here are some classroom-friendly methods:
- • Direct instruction: Structured and efficient—limits off-task time.
- • Inquiry-based learning: Encourages curiosity and responsibility.
- • Differentiated instruction: Tailors lessons to diverse needs, reducing frustration.
- • Project-based learning: Builds teamwork and engagement—great for restless classes.
A good teaching method keeps students interested, involved, and on-task, reducing the need for redirection.

You can also explore how gamification in education boosts engagement, reduces off‑task behavior, and reinforces classroom routines—see our detailed post on Gamification in Education.
Conclusion
Classroom management is both an art and a science. By using proven behaviour management techniques, addressing common problems of behaviour management, establishing consistent class rules, supporting positive behaviour , and selecting the right tools and styles of teaching, and teaching methods, teachers can create a learning space that’s structured, respectful, and productive.
It’s not about controlling students—it’s about guiding them. With patience, preparation, and the right strategies, management of behaviour in the classroom becomes a tool for empowerment, not punishment.
FAQs
1. What are the most effective behaviour management techniques in the classroom?
Effective techniques include positive reinforcement, non-verbal cues, proximity control, structured transitions, and offering choices. These strategies help maintain focus, reduce disruptions, and promote positive behaviour in the classroom.
2. What are common behaviour management problems faced by teachers?
Teachers often encounter issues like defiance, off-task behavior, frequent interruptions, talking out of turn, and lack of student engagement. These problems typically arise due to unclear class rules, inconsistent consequences, or mismatched teaching styles
3. How can class rules support behaviour management?
Clear and consistent rules in classroom set the tone for expected behaviour. They help students understand boundaries, provide structure, and create a safe, predictable learning environment. Rules should be simple and positively worded.
4. What is positive behaviour support and how does it work?
Positive behaviour support (PBS) is a proactive approach that focuses on teaching, modeling, and reinforcing desirable behaviours rather than punishing misbehaviour. It uses data to identify patterns and provides tiered support based on student needs.
5. How do teaching tools help with managing behaviour in the classroom?
Tools of teaching such as visual schedules, timers, behaviour tracking apps, and calm-down spaces help manage transitions, track behaviour, and reduce misunderstandings. They support structure and make expectations clear and engaging for students.
6. Which styles and methods of teaching are best for behaviour management?
Authoritative and democratic styles of teaching are often the most effective. As for the methods of teaching, approaches like differentiated instruction, direct teaching, and project-based learning keep students engaged and reduce behaviour issues by meeting diverse learning needs.